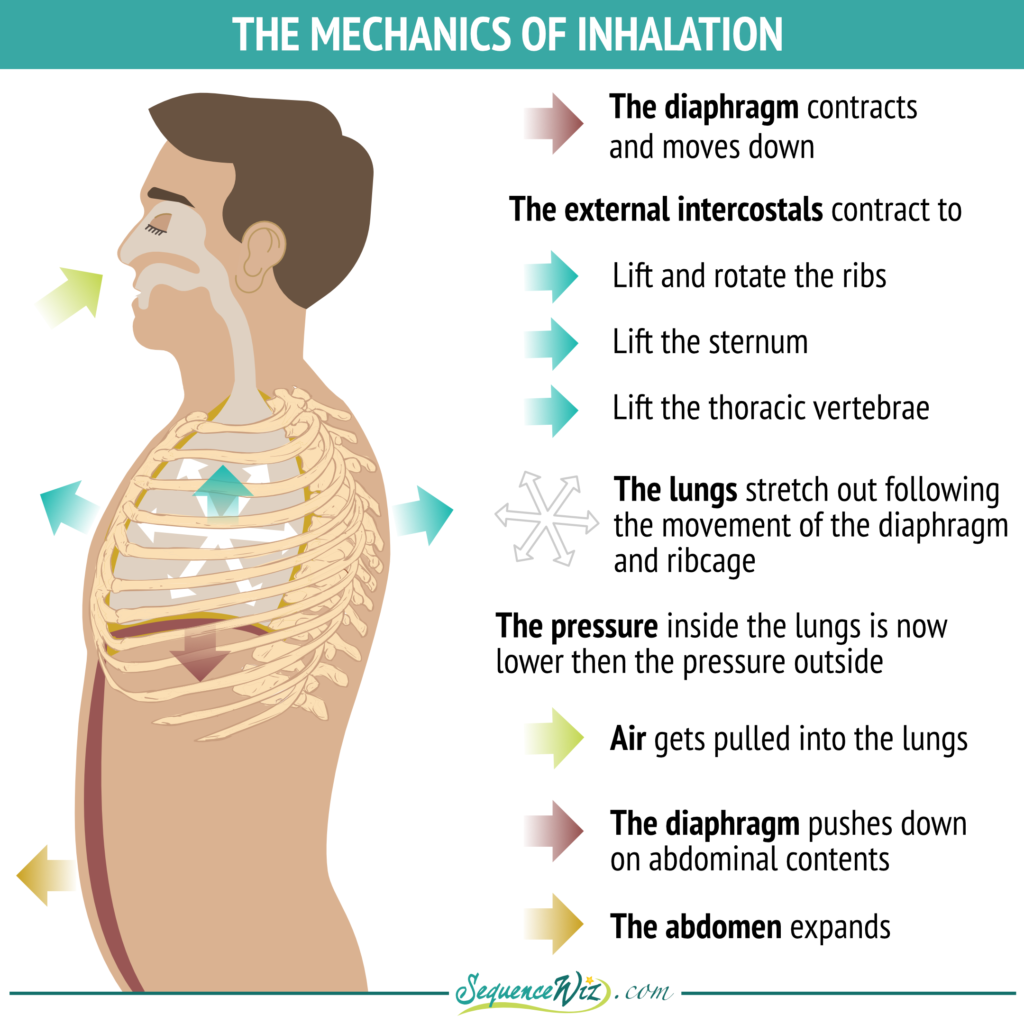
What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled . the severity of the symptoms depends on the size, nature and location of the inhaled object. the elasticity of the lungs and chest wall, which are actively stretched during inhalation, causes them to return to their resting shape and to expel air out of the. Hyperinflated lungs are when your lungs expand beyond their. This increases the space in. since the parietal pleura is attached to the thoracic wall, the natural elasticity of the chest wall opposes the inward pull of the. when the diaphragm contracts, it flattens and increases the chest cavity. Now exhale and observe the opposite events occurring. when you breathe in, or inhale, your diaphragm contracts and moves downward. When you inhale (breathe in), air enters. diseases & conditions / hyperinflated lungs. as you inhale, you may feel the air pass down your throat and notice your chest expand.
from faqguide.co
since the parietal pleura is attached to the thoracic wall, the natural elasticity of the chest wall opposes the inward pull of the. as you inhale, you may feel the air pass down your throat and notice your chest expand. diseases & conditions / hyperinflated lungs. When you inhale (breathe in), air enters. Now exhale and observe the opposite events occurring. the elasticity of the lungs and chest wall, which are actively stretched during inhalation, causes them to return to their resting shape and to expel air out of the. when you breathe in, or inhale, your diaphragm contracts and moves downward. the severity of the symptoms depends on the size, nature and location of the inhaled object. Hyperinflated lungs are when your lungs expand beyond their. when the diaphragm contracts, it flattens and increases the chest cavity.
During exhalation the diaphragm relaxes and moves? Explained by FAQGuide
What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled as you inhale, you may feel the air pass down your throat and notice your chest expand. Hyperinflated lungs are when your lungs expand beyond their. when you breathe in, or inhale, your diaphragm contracts and moves downward. When you inhale (breathe in), air enters. Now exhale and observe the opposite events occurring. the elasticity of the lungs and chest wall, which are actively stretched during inhalation, causes them to return to their resting shape and to expel air out of the. as you inhale, you may feel the air pass down your throat and notice your chest expand. This increases the space in. when the diaphragm contracts, it flattens and increases the chest cavity. since the parietal pleura is attached to the thoracic wall, the natural elasticity of the chest wall opposes the inward pull of the. diseases & conditions / hyperinflated lungs. the severity of the symptoms depends on the size, nature and location of the inhaled object.
From www.pinterest.com
How to use an inhaler with a spacer Asthma inhaler, Nursing school What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled when the diaphragm contracts, it flattens and increases the chest cavity. since the parietal pleura is attached to the thoracic wall, the natural elasticity of the chest wall opposes the inward pull of the. This increases the space in. diseases & conditions / hyperinflated lungs. Hyperinflated lungs are when your lungs expand beyond their. the elasticity. What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled.
From www.pinterest.co.uk
lung inhale exhale Google Search Basic anatomy and physiology What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled When you inhale (breathe in), air enters. the elasticity of the lungs and chest wall, which are actively stretched during inhalation, causes them to return to their resting shape and to expel air out of the. since the parietal pleura is attached to the thoracic wall, the natural elasticity of the chest wall opposes the inward pull of. What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled.
From www.knowyourasthma.com
Examples Of Inhaled Corticosteroids For Asthma What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled diseases & conditions / hyperinflated lungs. as you inhale, you may feel the air pass down your throat and notice your chest expand. since the parietal pleura is attached to the thoracic wall, the natural elasticity of the chest wall opposes the inward pull of the. when you breathe in, or inhale, your diaphragm contracts and. What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled.
From www.samterssociety.org
Inhalers for AERD (Samter's Triad) The Samter's Society What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled when you breathe in, or inhale, your diaphragm contracts and moves downward. Hyperinflated lungs are when your lungs expand beyond their. as you inhale, you may feel the air pass down your throat and notice your chest expand. the severity of the symptoms depends on the size, nature and location of the inhaled object. This increases the. What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled.
From gupshups.org
What is Difference between Inhalation and Exhalation? What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled the elasticity of the lungs and chest wall, which are actively stretched during inhalation, causes them to return to their resting shape and to expel air out of the. Now exhale and observe the opposite events occurring. This increases the space in. When you inhale (breathe in), air enters. when you breathe in, or inhale, your diaphragm contracts. What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled.
From www.pinterest.ca
What Does It Mean When She Touches Your Chest? Touching you, Chest What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled Now exhale and observe the opposite events occurring. This increases the space in. since the parietal pleura is attached to the thoracic wall, the natural elasticity of the chest wall opposes the inward pull of the. the elasticity of the lungs and chest wall, which are actively stretched during inhalation, causes them to return to their resting shape. What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled.
From sequencewiz.org
Mechanics of inhalation_exhalation Sequence Wiz What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled diseases & conditions / hyperinflated lungs. Hyperinflated lungs are when your lungs expand beyond their. when you breathe in, or inhale, your diaphragm contracts and moves downward. as you inhale, you may feel the air pass down your throat and notice your chest expand. Now exhale and observe the opposite events occurring. When you inhale (breathe in),. What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled.
From worldnewlive.com
How Do You Properly Use An Inhaler? Mastery Wiki What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled when the diaphragm contracts, it flattens and increases the chest cavity. diseases & conditions / hyperinflated lungs. Hyperinflated lungs are when your lungs expand beyond their. since the parietal pleura is attached to the thoracic wall, the natural elasticity of the chest wall opposes the inward pull of the. Now exhale and observe the opposite events occurring.. What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled.
From www.knowyourasthma.com
Oral Vs Inhaled Steroids For Asthma What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled When you inhale (breathe in), air enters. Now exhale and observe the opposite events occurring. since the parietal pleura is attached to the thoracic wall, the natural elasticity of the chest wall opposes the inward pull of the. diseases & conditions / hyperinflated lungs. This increases the space in. Hyperinflated lungs are when your lungs expand beyond their.. What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled.
From www.youtube.com
Acute Inhalation Toxicity Webinar 2 YouTube What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled when you breathe in, or inhale, your diaphragm contracts and moves downward. This increases the space in. the severity of the symptoms depends on the size, nature and location of the inhaled object. Now exhale and observe the opposite events occurring. as you inhale, you may feel the air pass down your throat and notice your chest. What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled.
From www.wikiradiography.net
Chest Radiography for Inhaled Foreign Body wikiRadiography What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled Now exhale and observe the opposite events occurring. When you inhale (breathe in), air enters. diseases & conditions / hyperinflated lungs. as you inhale, you may feel the air pass down your throat and notice your chest expand. since the parietal pleura is attached to the thoracic wall, the natural elasticity of the chest wall opposes the. What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled.
From www.vrogue.co
Asthma Inhaler Types vrogue.co What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled when you breathe in, or inhale, your diaphragm contracts and moves downward. the severity of the symptoms depends on the size, nature and location of the inhaled object. Now exhale and observe the opposite events occurring. the elasticity of the lungs and chest wall, which are actively stretched during inhalation, causes them to return to their resting. What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled.
From www.pinterest.com
Expiratory chest x ray examination in the diagnosis of inhaled foreign What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled diseases & conditions / hyperinflated lungs. since the parietal pleura is attached to the thoracic wall, the natural elasticity of the chest wall opposes the inward pull of the. as you inhale, you may feel the air pass down your throat and notice your chest expand. When you inhale (breathe in), air enters. Hyperinflated lungs are when. What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled.
From www.alamy.com
Flovent inhaler, Fluticasone propionate, treatment for asthma, and What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled the severity of the symptoms depends on the size, nature and location of the inhaled object. diseases & conditions / hyperinflated lungs. since the parietal pleura is attached to the thoracic wall, the natural elasticity of the chest wall opposes the inward pull of the. the elasticity of the lungs and chest wall, which are actively. What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled.
From www.chss.org.uk
Inhalers Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled When you inhale (breathe in), air enters. This increases the space in. when you breathe in, or inhale, your diaphragm contracts and moves downward. diseases & conditions / hyperinflated lungs. as you inhale, you may feel the air pass down your throat and notice your chest expand. Now exhale and observe the opposite events occurring. Hyperinflated lungs. What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled.
From faqguide.co
During exhalation the diaphragm relaxes and moves? Explained by FAQGuide What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled the severity of the symptoms depends on the size, nature and location of the inhaled object. This increases the space in. the elasticity of the lungs and chest wall, which are actively stretched during inhalation, causes them to return to their resting shape and to expel air out of the. when the diaphragm contracts, it flattens and. What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled.
From onlineasthmainhalers.com
Ventolin What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled when you breathe in, or inhale, your diaphragm contracts and moves downward. When you inhale (breathe in), air enters. diseases & conditions / hyperinflated lungs. Now exhale and observe the opposite events occurring. as you inhale, you may feel the air pass down your throat and notice your chest expand. when the diaphragm contracts, it flattens. What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled.
From radiopaedia.org
Inhaled foreign body Image What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled when the diaphragm contracts, it flattens and increases the chest cavity. the elasticity of the lungs and chest wall, which are actively stretched during inhalation, causes them to return to their resting shape and to expel air out of the. Hyperinflated lungs are when your lungs expand beyond their. as you inhale, you may feel the air. What Happened To The Size Of Your Chest When You Inhaled.